Decoding the Enigma: Phasor Diagrams in RLC Circuits
Ever feel like electrical circuits are speaking a secret language? Like a cryptic code you just can't crack? Well, you're not alone. Understanding the behavior of alternating current in circuits with resistors, inductors, and capacitors – RLC circuits – can be a real head-scratcher. But there's a secret weapon: the phasor diagram. It’s the Rosetta Stone for deciphering these complex electrical relationships.
Imagine trying to juggle three balls at once – the voltage across a resistor, the voltage across an inductor, and the voltage across a capacitor. Each voltage is changing constantly, and they're not even in sync! That's what's happening in an RLC circuit. Phasor diagrams offer a visual snapshot, freezing this dynamic interplay so we can analyze it.
A phasor diagram isn't a literal picture of the circuit; it's more like a stylish, abstract representation. It uses rotating vectors, called phasors, to represent the voltages and currents. The length of the phasor corresponds to the magnitude, and its angle represents the phase difference. This elegant visualization helps us understand how the different components contribute to the overall circuit behavior.
Historically, analyzing AC circuits before phasor diagrams was like navigating a city without a map. Imagine trying to calculate total impedance without a visual aid! Early electrical engineers relied on complex algebraic equations, which could quickly become unwieldy. Phasor diagrams emerged as a powerful tool for simplifying these calculations, providing a more intuitive understanding of circuit dynamics.
So, why are phasor diagrams for RLC circuit analysis so important? They’re crucial for understanding resonance, a phenomenon where the circuit's impedance is minimized. This has major implications for things like radio tuning, where you want to select a specific frequency. Without phasor diagrams, understanding and predicting resonance would be significantly more challenging.
Let's break down a simple example. In a series RLC circuit, the voltage across the resistor is in phase with the current. The voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90 degrees, and the voltage across the capacitor lags the current by 90 degrees. A phasor diagram neatly captures these phase relationships, making it easy to see how they combine to determine the overall circuit impedance.
Here are some key benefits of using phasor diagrams in RLC circuit analysis: simplified calculations, improved understanding of phase relationships, and easier prediction of resonance frequencies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simplifies complex AC circuit analysis | Limited to steady-state sinusoidal analysis |
| Visually represents phase relationships | Can be challenging to visualize for complex circuits |
| Facilitates understanding of resonance | Does not provide information about transient behavior |
Best Practices:
1. Always label your phasors clearly.
2. Use a consistent scale for the magnitudes.
3. Indicate the direction of rotation.
4. Choose a reference phasor (usually the current).
5. Carefully consider the phase relationships between different components.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a phasor? A rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. Why do we use phasor diagrams? To simplify AC circuit analysis.
3. What is resonance? A condition where the circuit's impedance is minimized.
4. How do I determine the phase angle? By comparing the phase of the voltage and current.
5. What is impedance? The total opposition to current flow in an AC circuit.
6. How do phasors represent different frequencies? The frequency is implicit in the angular velocity of the phasor.
7. Can phasor diagrams be used for non-sinusoidal waveforms? No, they are specifically for sinusoidal waveforms.
8. What's the difference between a phasor and a vector? A phasor represents a time-varying quantity, while a vector represents a static quantity.
Tips and tricks: Remember to always choose a reference phasor, typically the current. This helps to maintain consistency and avoid confusion.
In conclusion, phasor diagrams are an essential tool for anyone working with RLC circuits. They provide a powerful visual language for understanding complex AC circuit behavior, simplifying calculations, and making sense of phase relationships. From radio tuning to power systems, phasor diagrams are vital for designing and analyzing a wide range of electrical systems. Mastering this technique empowers you to unlock the secrets of circuit dynamics and navigate the intricate world of electrical engineering. So, dive into the world of phasors – you might be surprised at how much easier it makes understanding these seemingly complex circuits! Embrace the visual elegance and analytical power of phasor diagrams, and watch the mysteries of RLC circuits unravel before your eyes.

Series RLC Circuit Circuit Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram Of Rlc Circuit At Resonance | Taqueria Autentica

Series Rlc Circuit Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Rlc Circuit Phase Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Parallel RLC Circuit Impedance | Taqueria Autentica

Draw Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit | Taqueria Autentica
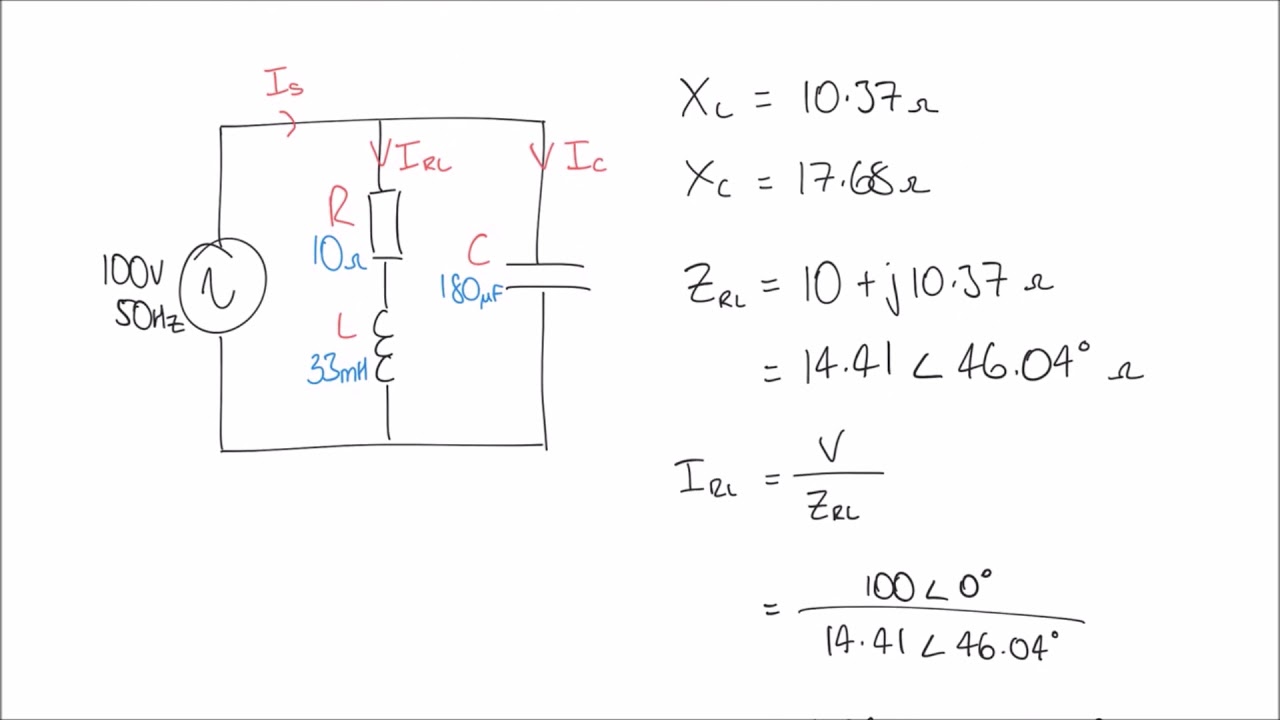
Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit At Resonance | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

Circuit Power Factor Calculator | Taqueria Autentica

Phase Diagram Of Rl Circuit | Taqueria Autentica
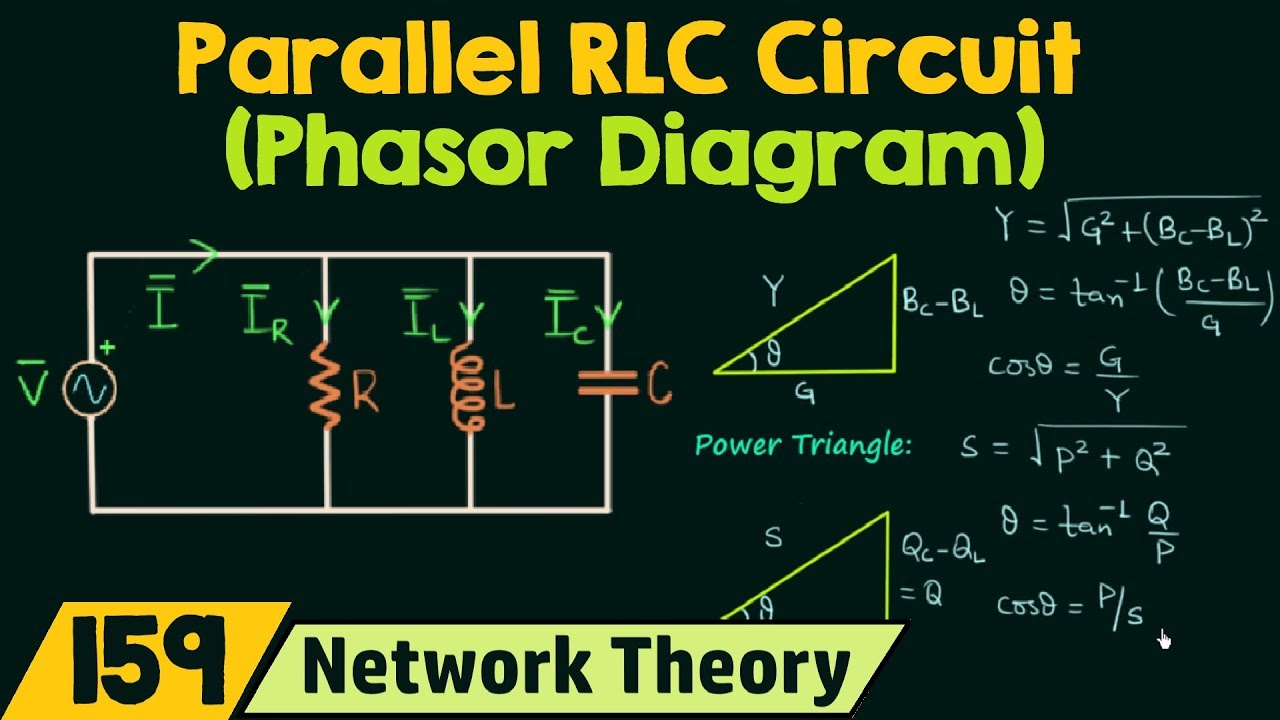
Phasor Diagram For Parallel Rlc Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

What is RLC Series Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram Derivation | Taqueria Autentica
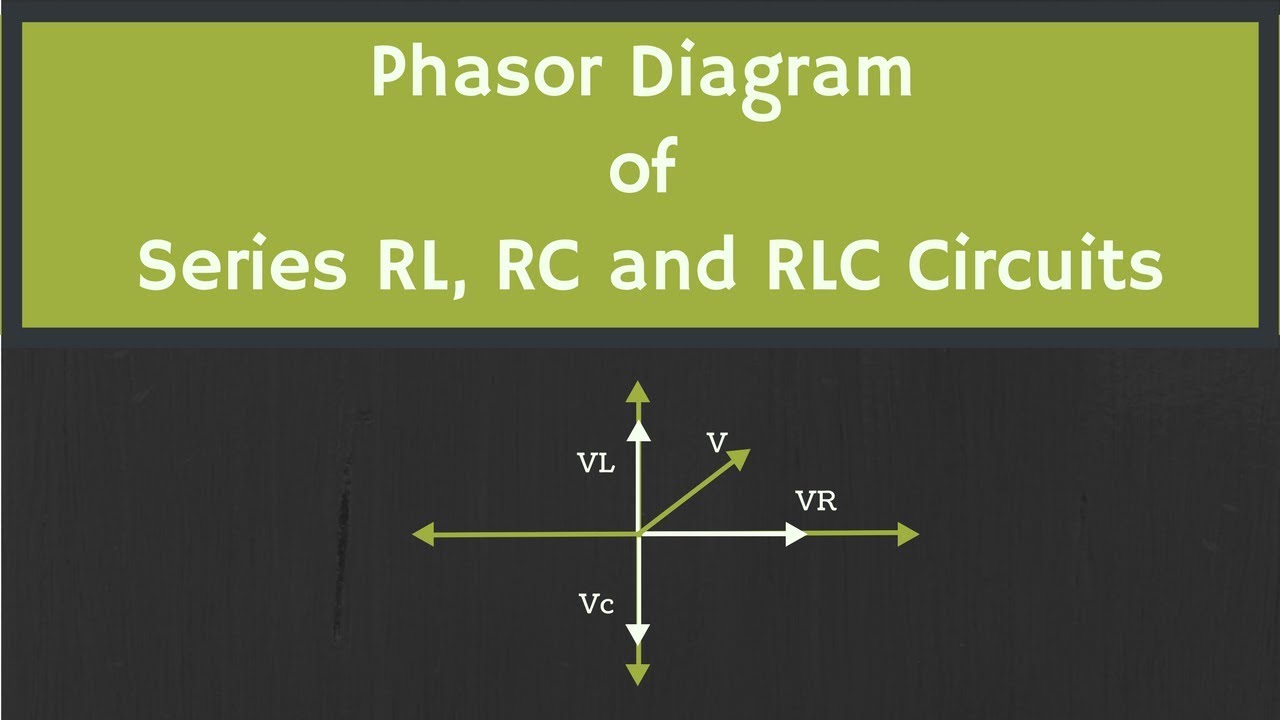
Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit Series | Taqueria Autentica

What is RLC Series Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram Derivation | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit Pdf | Taqueria Autentica