The Subtle Art of Pneumatic System Conductors
There's a quiet elegance to the way a pneumatic system functions, a symphony of compressed air powering intricate movements. At the heart of this silent ballet lies the pneumatic system conductor – the unsung hero, the essential conduit that orchestrates the flow of energy. It’s the subtle details that matter, the precision and reliability that truly define a well-designed pneumatic system, and the conductor plays a crucial role.
Think of the conductor as the arteries of a pneumatic system, channeling the lifeblood of compressed air to power cylinders, valves, and other components. Without this vital network, the system would be inert, unable to perform its designated task. Whether it’s a robotic arm on an assembly line or the brakes on a heavy-duty truck, the conductor ensures the seamless transfer of power, enabling these systems to function with precision and efficiency.
The story of pneumatic conductors begins with the understanding of compressed air as a power source. From early industrial applications to modern-day robotics, the need for efficient air transfer has driven the evolution of conductor design. Initially, simple pipes and tubes served this purpose, but advancements in materials and manufacturing have led to the development of more sophisticated conductors, including flexible hoses, tubing bundles, and quick-connect fittings. These modern conduits not only improve efficiency but also enhance the overall flexibility and adaptability of pneumatic systems.
The importance of a well-designed pneumatic conductor system cannot be overstated. It directly impacts the system's performance, reliability, and longevity. A poorly designed system can lead to leaks, pressure drops, and component damage, ultimately compromising the entire operation. This is why careful consideration must be given to the selection, installation, and maintenance of pneumatic conductors.
One of the primary challenges in pneumatic conductor design is minimizing air leakage. Even small leaks can accumulate, leading to significant energy waste and reduced system performance. Properly sealed connections, high-quality tubing materials, and regular maintenance are essential for mitigating this issue. Furthermore, the conductor's size and configuration play a vital role in maintaining optimal air pressure and flow rate. Selecting the right diameter and length is crucial for ensuring efficient power delivery to the actuators.
Pneumatic conductors are typically classified based on their material, flexibility, and pressure rating. Common materials include polyurethane, nylon, and various polymers. Flexible conductors, such as hoses, offer greater adaptability for complex system layouts, while rigid tubing provides a more permanent and robust solution. Understanding the different types of conductors and their specific characteristics is essential for selecting the appropriate components for a given application.
Three key benefits of well-designed pneumatic conductors are: efficiency, reliability, and adaptability. Efficient conductors minimize pressure drops and leaks, maximizing the power delivered to the actuators and reducing energy consumption. Reliable conductors ensure consistent and predictable performance, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. Adaptable conductor systems can be easily modified or expanded to accommodate changes in system requirements or layout.
Ensuring optimal performance of your pneumatic conductor systems involves regular inspections, leak detection, and timely replacement of worn components. A simple checklist can be helpful: regularly check for leaks, visually inspect the tubing for damage, and verify proper connection tightness. Implement a preventative maintenance schedule based on the system's operating conditions and manufacturer's recommendations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Pneumatic Conductor Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Polyurethane | Flexibility, abrasion resistance | Limited temperature range |
| Nylon | Strength, chemical resistance | Less flexible than polyurethane |
Best Practices for Pneumatic Conductor Systems:
1. Proper Sizing: Select the appropriate conductor diameter to minimize pressure drop and ensure efficient airflow.
2. Material Selection: Choose a conductor material compatible with the operating environment and the type of air being used.
3. Leak Prevention: Use high-quality fittings and ensure proper installation to minimize leaks.
4. Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect the system for signs of wear, damage, or leaks.
5. Proper Routing: Design the conductor layout to minimize bends and restrictions, ensuring smooth airflow.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the most common type of pneumatic conductor? Answer: Flexible tubing made of polyurethane or nylon is commonly used.
2. How do I choose the right size conductor? Answer: Consider the airflow requirements, pressure, and distance.
3. How can I prevent leaks in my pneumatic system? Answer: Ensure proper fitting installation and use high-quality sealing materials.
4. What are the signs of a failing pneumatic conductor? Answer: Leaks, kinks, or visible damage.
5. How often should I inspect my pneumatic conductor system? Answer: Regular inspections are recommended, based on the operating conditions.
6. What are the different types of pneumatic fittings available? Answer: Push-to-connect, compression, and threaded fittings are common.
7. What is the role of a lubricator in a pneumatic system? Answer: Lubricators introduce oil into the airflow to reduce friction and extend component life.
8. How does temperature affect pneumatic conductors? Answer: Extreme temperatures can impact the performance and lifespan of certain conductor materials.
Tips and Tricks: Use color-coded tubing to identify different air lines within a complex system. Regularly drain moisture from the air compressor and receiver to prevent condensation buildup in the conductors.
In conclusion, the pneumatic system conductor, often overlooked, plays a critical role in the efficiency, reliability, and overall performance of any pneumatic system. From powering industrial machinery to operating delicate robotic arms, the seamless transfer of compressed air relies on the integrity and efficiency of these conduits. Understanding the nuances of conductor selection, installation, and maintenance is paramount for maximizing system performance and minimizing downtime. By prioritizing these often-unseen components, we ensure the smooth operation of countless applications that rely on the silent power of compressed air. Investing in high-quality conductors and adhering to best practices will not only enhance system performance but also contribute to long-term cost savings and improved operational efficiency. Take the time to assess your current pneumatic systems, and ensure that your conductors are up to the task, enabling the quiet symphony of compressed air to power your operations effectively.

Basic Pneumatic Symbols Pdf | Taqueria Autentica

conductor for pneumatic systems | Taqueria Autentica

Pneumatic Circuit Valve Symbols at Luis Abbott blog | Taqueria Autentica

Pneumatic Circuit Diagram Symbols | Taqueria Autentica

Hydraulic Symbols Pneumatic Symbol Library Hydraulics | Taqueria Autentica

Double acting integral type pneumatic cylinders rear flange mounted | Taqueria Autentica
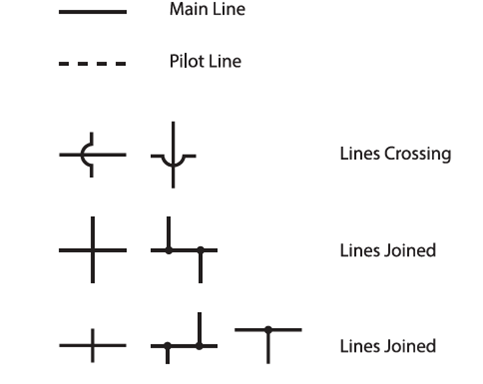
Common Symbols Used in Pneumatic Systems and Instrumentations | Taqueria Autentica
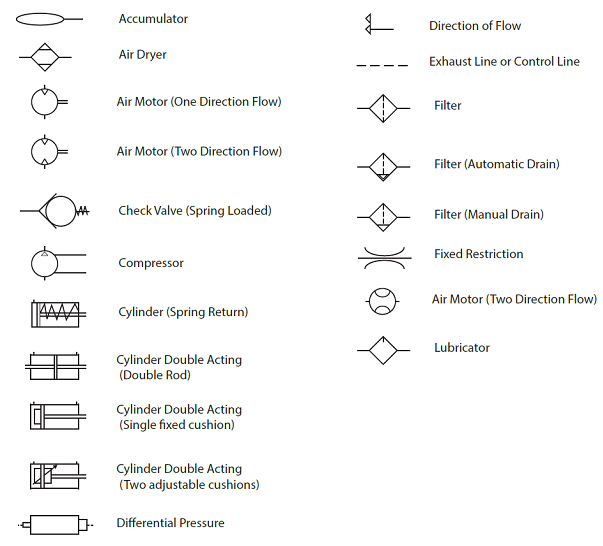
How To Read Pneumatic Diagrams | Taqueria Autentica

conductor for pneumatic systems | Taqueria Autentica

conductor for pneumatic systems | Taqueria Autentica

Lot Gabbiani TDA 10480 electronic squaring machine | Taqueria Autentica

Vacuum Regulator Symbol at Karl Spiker blog | Taqueria Autentica

Basic Symbols Of Pneumatic Systems | Taqueria Autentica
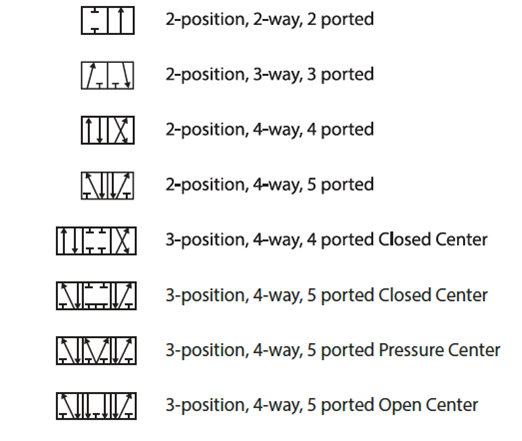
conductor for pneumatic systems | Taqueria Autentica

Where to Buy Aftermarket Parts in Canada | Taqueria Autentica