Unlocking Automation: Demystifying PIR Sensor Module Circuit Diagrams
Ever walked into a room and the lights magically flickered on? That's the subtle power of a Passive Infrared (PIR) sensor. These ingenious devices are the backbone of countless automated systems, from security lights to automatic doors. Understanding the PIR sensor module circuit diagram is key to harnessing their potential and incorporating them into your own projects.
At its core, a PIR sensor detects changes in infrared radiation. Everything emits some level of infrared, and when a warm body like a person or animal moves within the sensor's range, it triggers a change in the infrared signature. This change is then amplified and processed by the circuit, ultimately activating an output signal. The PIR sensor wiring diagram provides a roadmap to understanding this intricate process.
The PIR sensor's journey from a niche technology to a ubiquitous component is fascinating. Initially developed for military applications, these sensors soon found their way into commercial and domestic settings. The increasing demand for automation and energy efficiency propelled their adoption, leading to miniaturization, cost reduction, and enhanced sensitivity. Understanding the PIR sensor module connection diagram is crucial for effectively utilizing these advancements.
The significance of the PIR sensor module schematic extends beyond simple motion detection. Its low power consumption, ease of integration, and affordability make it a versatile tool for various applications. However, issues like false triggering due to environmental factors or incorrect placement can pose challenges. A thorough understanding of the PIR sensor module circuit diagram is essential for mitigating these issues.
Delving into the PIR sensor module electronic diagram reveals a combination of sensitive pyroelectric elements, amplifiers, comparators, and timers. The pyroelectric elements convert infrared radiation into electrical signals. These signals are amplified and compared to a threshold value. If the change in infrared radiation exceeds this threshold, the comparator triggers the output, activating a relay or other connected devices. The timing circuit controls the duration of the output signal.
A simple example is a motion-activated light switch. When someone enters the room, the PIR sensor detects the change in infrared radiation and triggers the output, turning on the light. After a preset duration, if no further motion is detected, the output deactivates, turning the light off. This seemingly simple operation is orchestrated by the intricacies of the PIR sensor module electrical diagram.
Three key benefits of utilizing PIR sensors stem from their inherent design: energy conservation, enhanced security, and improved convenience. Energy is conserved by automating lighting and appliances based on occupancy. Security is enhanced by triggering alarms or notifications upon detecting motion. Convenience is improved by automating tasks like opening doors or activating appliances without physical interaction.
If you encounter issues with a PIR sensor, troubleshooting often involves checking the power supply, verifying connections based on the PIR sensor module wiring schematic, adjusting sensitivity, and ensuring proper placement to avoid false triggers. A clear understanding of the PIR sensor module circuit diagram is essential for effective diagnosis and resolution.
For those eager to explore the practical application of PIR sensors, a basic project could involve creating a motion-activated LED light. The PIR sensor module connection diagram will guide you through connecting the sensor to an Arduino or other microcontroller, an LED, and a power source. Programming the microcontroller to activate the LED upon receiving a signal from the sensor brings the project to life.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PIR Sensors
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low Power Consumption | Susceptibility to False Triggers |
| Easy Integration | Limited Range and Field of View |
| Cost-Effective | Performance Affected by Temperature Extremes |
Best practices for implementing PIR sensors include choosing the right sensor for the application, considering the environment and potential sources of interference, ensuring proper mounting and alignment, adjusting sensitivity appropriately, and testing thoroughly after installation.
Real-world examples of PIR sensor applications include automatic lighting systems in homes and offices, security alarms triggered by motion detection, automatic door openers in commercial buildings, wildlife cameras activated by animal movement, and touchless faucets in public restrooms.
Challenges associated with PIR sensors, such as false triggering due to pets or sunlight, can be addressed by adjusting sensitivity, masking specific areas of the sensor's field of view, and utilizing temperature compensation features. Issues with limited range can be overcome by strategically placing multiple sensors or using sensors with a wider field of view. Understanding the PIR sensor module circuit diagram aids in resolving such challenges effectively.
Frequently asked questions about PIR sensors often revolve around their range, sensitivity, power requirements, mounting options, and troubleshooting common issues. Online resources and forums provide a wealth of information for addressing these queries.
Tips and tricks for maximizing PIR sensor performance include optimizing placement for optimal coverage, adjusting sensitivity to minimize false triggers, using lenses or reflectors to focus the sensor's field of view, and incorporating temperature compensation for improved accuracy.
In conclusion, the PIR sensor module circuit diagram serves as a fundamental blueprint for understanding and utilizing these versatile devices. From automating simple tasks to enhancing security and conserving energy, PIR sensors have become an integral part of modern technology. By delving into the intricacies of the PIR sensor schematic and exploring its various applications, you unlock the potential to create innovative and efficient automated systems. Embrace the power of motion detection and embark on your journey to explore the boundless possibilities of PIR technology. This understanding empowers you to troubleshoot issues, optimize performance, and seamlessly integrate PIR sensors into a wide range of projects, from DIY home automation to complex industrial systems. The future of automation is motion-sensitive, and with a grasp of the PIR sensor module circuit diagram, you're well-equipped to shape that future.
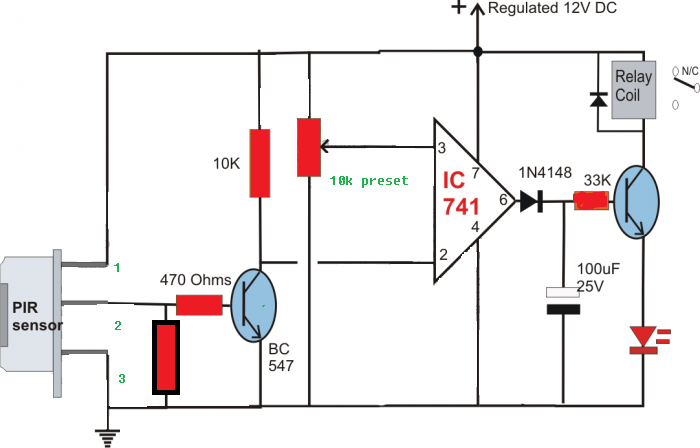
Pyroelectric Infrared Sensor Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Motion Sensor Led Light Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

PIR Sensor Security Light Switch | Taqueria Autentica

Motion Sensor Light Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

Pir Motion Sensor Arduino Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Staroveku výbuch my sami pir sensor switch circuit sadenice spoliehať | Taqueria Autentica

pir sensor module circuit diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Simple Pir Sensor Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

pir sensor module circuit diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Pir Sensor Relay Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica
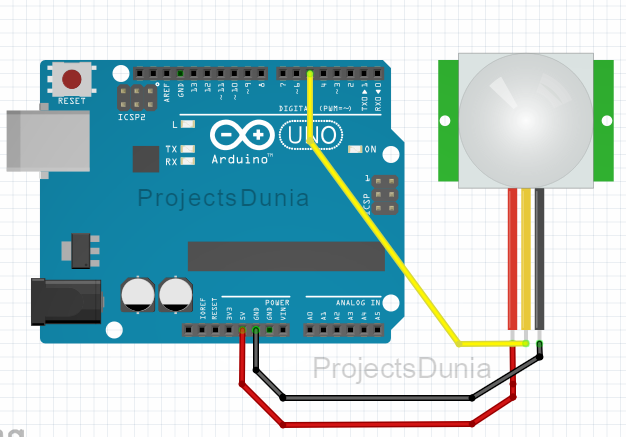
Pir Based Motion Sensor Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica
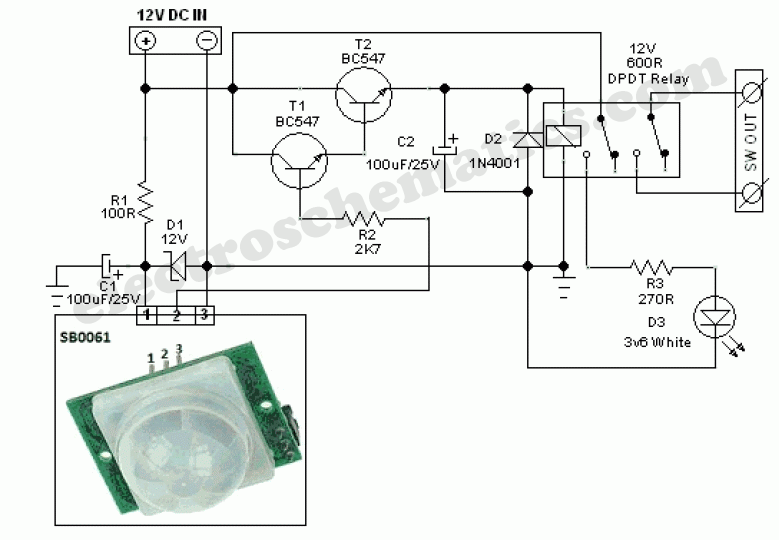
Motion Sensor Circuit Diagram Pdf | Taqueria Autentica

Motion Sensor Trigger Switch at Norma Gray blog | Taqueria Autentica

How does an HC | Taqueria Autentica
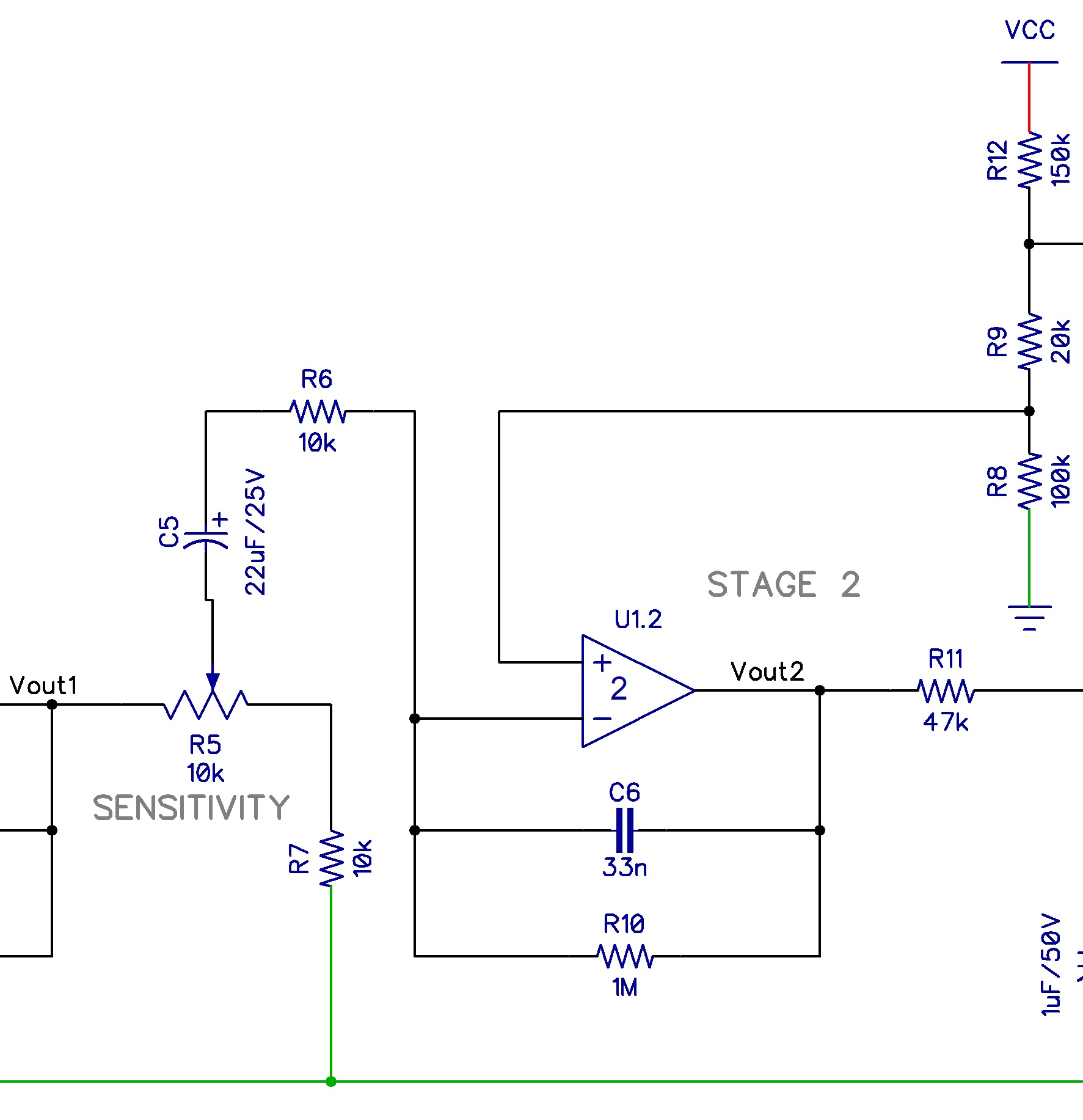
Pir Sensor Circuit Diagram | Taqueria Autentica