Unlocking Circuit Secrets: Mastering LR Circuit Phasor Diagrams
Ever felt lost navigating the complexities of AC circuits? Imagine a visual roadmap that simplifies the intricate dance of voltage and current in an inductor-resistor circuit. That's the power of the LR circuit phasor diagram. It's not just a theoretical concept; it's a practical tool that unlocks a deeper understanding of circuit behavior and empowers you to design and analyze circuits with confidence.
An LR circuit, a fundamental building block in electrical engineering, combines an inductor (L) and a resistor (R). When an alternating current flows through this circuit, the inductor's opposition to changes in current and the resistor's inherent resistance create a phase difference between voltage and current. This dynamic interaction is elegantly captured by the LR circuit phasor diagram, a graphical representation that uses vectors (phasors) to depict the magnitude and phase relationship between voltage and current.
Understanding these diagrams is crucial for anyone working with AC circuits. They provide a visual shortcut to complex calculations, allowing you to quickly determine the overall impedance of the circuit, the power factor, and the voltage drops across individual components. This knowledge is essential for designing efficient and reliable circuits, from simple filters to complex power systems.
Historically, phasor diagrams emerged as a powerful tool for simplifying AC circuit analysis before the widespread availability of sophisticated computer simulations. Their intuitive visual nature makes them invaluable for educational purposes, providing a clear and concise way to grasp the fundamental principles of AC circuit behavior. While advanced software can now perform complex calculations, the underlying principles visualized by phasor diagrams remain fundamental to electrical engineering.
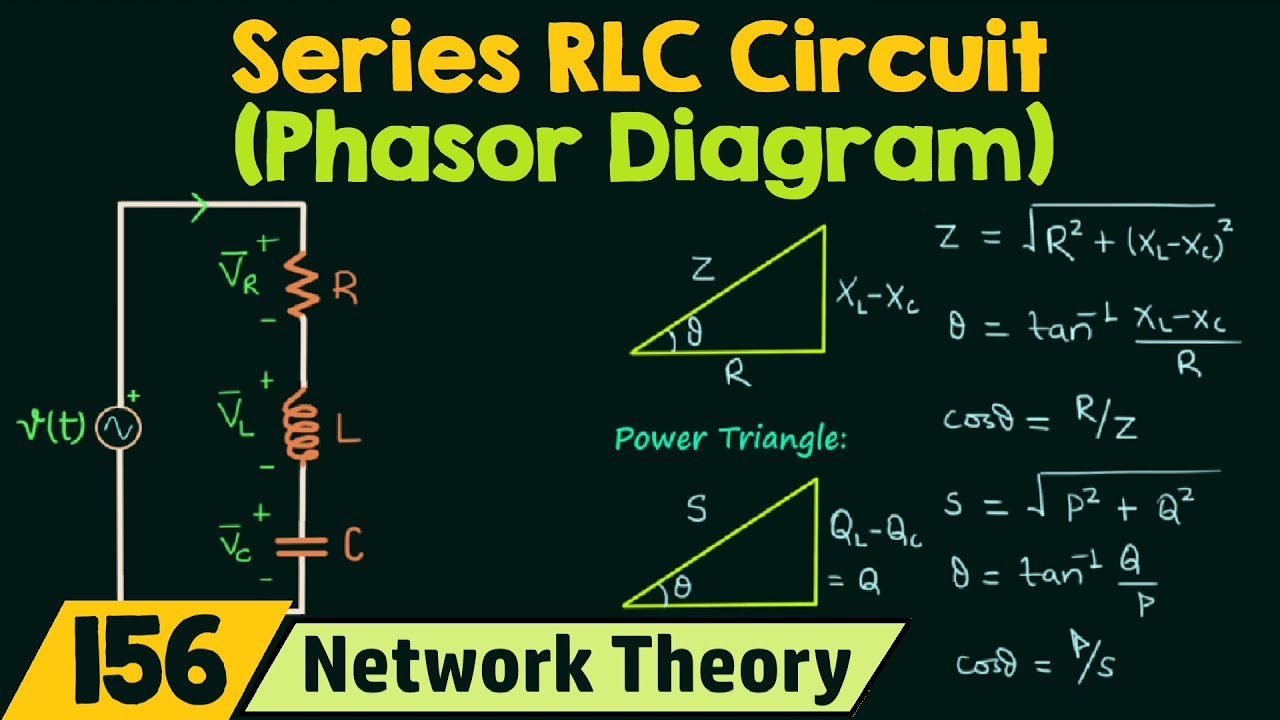
One of the main challenges related to LR circuit phasor diagrams is understanding the concept of phase shift. The inductor's opposition to changes in current causes the current to lag behind the voltage. This lag, represented by an angle (phi) in the phasor diagram, is crucial for accurate circuit analysis. Mastering this concept opens the door to understanding the overall impedance of the circuit, a key parameter that determines how the circuit responds to different frequencies.
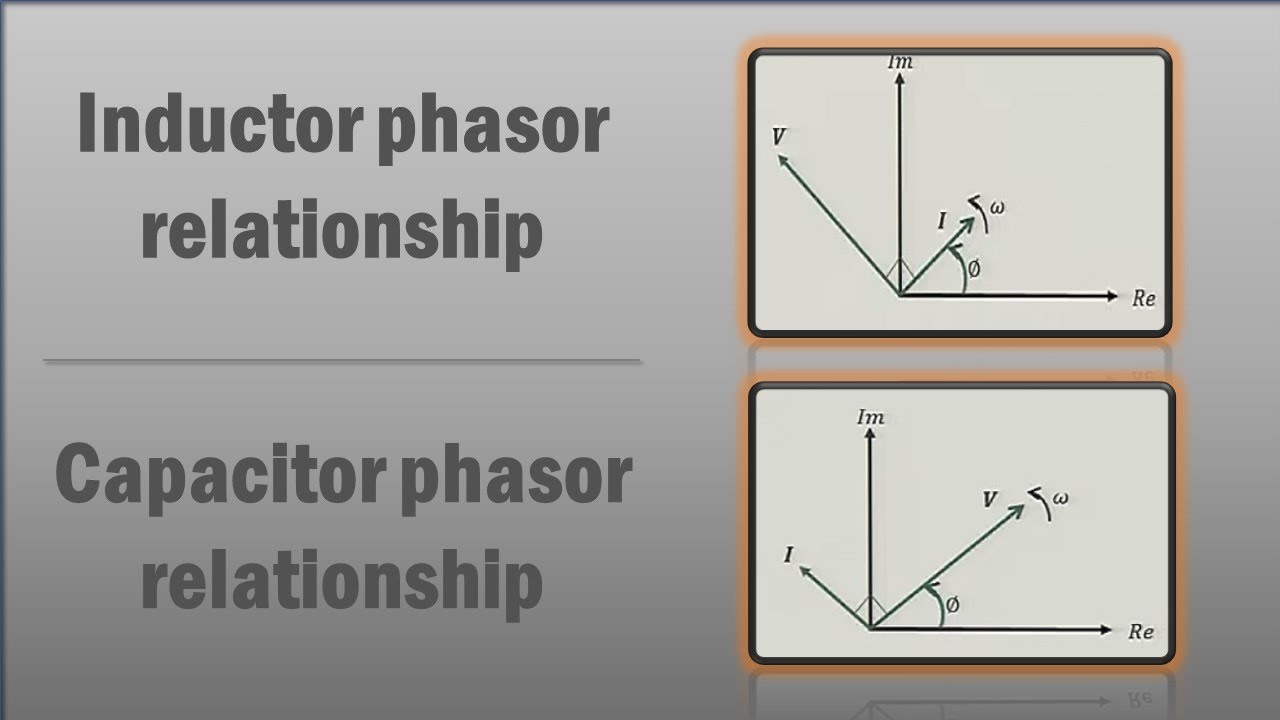
In an LR circuit phasor diagram, the resistor's voltage and current are in phase, represented by phasors pointing in the same direction. The inductor's voltage leads the current by 90 degrees, depicted by a phasor rotated counterclockwise. The resultant voltage across the entire LR circuit is the vector sum of these individual voltage phasors. For example, if the resistor voltage is 3V and the inductor voltage is 4V, the total voltage isn't simply 7V. You need to use vector addition, considering the 90-degree phase difference, to find the actual magnitude of the total voltage.
Three key benefits of understanding LR circuit phasor diagrams are: simplified impedance calculation, power factor determination, and enhanced circuit design. Phasor diagrams visually represent impedance as the vector sum of resistance and inductive reactance. This simplifies calculations compared to using complex numbers. The power factor, representing the efficiency of power transfer, can be easily derived from the phase angle in the diagram. Lastly, a clear understanding of phasor diagrams aids in designing circuits with desired frequency responses, crucial in applications like filters and resonant circuits.
To construct an LR circuit phasor diagram, first, draw the resistor voltage phasor horizontally. Then, draw the inductor voltage phasor 90 degrees counterclockwise from the resistor voltage phasor. The vector sum of these two phasors represents the total circuit voltage. The current phasor is aligned with the resistor voltage phasor.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LR Circuit Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Visual representation simplifies understanding | Can be complex for circuits with many components |
| Facilitates quick calculations of impedance and power factor | Limited to steady-state analysis |
| Aids in circuit design and optimization | Doesn't directly show transient behavior |
Best practices include: always drawing the resistor voltage horizontally, ensuring the inductor voltage leads the current by 90 degrees, and clearly labeling all phasors with their respective magnitudes and units. Real-world examples of LR circuits include filter circuits in audio equipment and power factor correction circuits in industrial settings. Challenges in understanding these diagrams often relate to grasping the concept of phase shift and vector addition, but practice and visual aids can overcome these hurdles.
FAQs: What is a phasor? (A vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.) What is impedance? (The total opposition to current flow in an AC circuit.) What is the power factor? (The ratio of real power to apparent power.) Why does the inductor voltage lead the current? (Due to the inductor's back EMF opposing changes in current.)
One helpful tip is to use different colors for voltage and current phasors to enhance visual clarity. Software tools and online simulators can also provide interactive visualizations of LR circuit behavior, further solidifying understanding.
In conclusion, LR circuit phasor diagrams are indispensable tools for anyone working with AC circuits. They provide a visual pathway to understanding the complex interplay of voltage and current, simplifying circuit analysis and design. While mastering the concept of phase shift and vector addition might initially pose a challenge, the benefits of understanding these diagrams are substantial. They empower you to calculate impedance, determine power factor, and design circuits with specific frequency responses. By embracing the power of visualization, you can unlock a deeper understanding of AC circuit behavior and confidently tackle the challenges of circuit analysis and design. So, dive into the world of LR circuit phasor diagrams and empower yourself with the knowledge to conquer the complexities of AC circuits. Explore online resources, practice drawing diagrams, and unlock the potential of this powerful analytical tool.

Phasor Diagram For Series Rl Circuit | Taqueria Autentica
Phasor Diagram Ac Circuit | Taqueria Autentica
Phasor Diagram Of Inductor In Ac Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

Lr Circuit Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Phase Diagram Of Lr Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

716 Phasor diagram for series LR | Taqueria Autentica

Phase Diagram Of Lr Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Representation Of One Phase AC Circuit Presentation | Taqueria Autentica

What is RL Series Circuit Circuit Diagram Phasor Diagram Derivation | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagrams Of Ac Circuits | Taqueria Autentica

How To Draw Phasor Diagram at How To Draw | Taqueria Autentica

Phase Diagram Of Lr Circuit | Taqueria Autentica
How To Solve Lcr Circuit at Rebbecca Lohman blog | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram Of Rl Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram Rlc Circuit | Taqueria Autentica