Unlocking the Secrets of Shaft Key Sizing: A Deep Dive
Ever wonder how rotating machinery transfers power so efficiently? The secret often lies in a small but mighty component: the shaft key. This unassuming piece of metal, nestled within a keyway cut into both the shaft and the hub, is the linchpin that connects rotating components and enables the transmission of torque. Understanding the relationship between key size and shaft diameter is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient power transfer in everything from industrial machinery to automotive drivetrains.
Selecting the correct key dimensions for a given shaft diameter is not a trivial matter. An undersized key can shear under load, leading to catastrophic failure, while an oversized key can weaken the shaft, making it susceptible to fatigue and fracture. This delicate balance underscores the importance of precise key size selection. This article delves into the intricacies of shaft key sizing, offering a comprehensive guide to this critical aspect of mechanical engineering.
The historical development of shaft keys traces back to the earliest days of machinery, evolving alongside advancements in materials and manufacturing techniques. Initially, simple square or rectangular keys were common. Over time, standardized key designs emerged, like the Woodruff key and the parallel key, each with its own advantages and applications. The importance of proper key dimensioning was quickly recognized as crucial for preventing equipment failure and improving overall performance.
One of the main challenges associated with keyway sizing is achieving the optimal balance between strength and shaft integrity. The keyway itself introduces a stress concentration in the shaft, which can become a point of weakness. Proper key size selection, combined with careful keyway design and manufacturing, minimizes this risk while ensuring adequate power transmission capacity.
The key size for a particular shaft diameter isn't arbitrary. Standardized tables and formulas, like those provided in ANSI and ISO standards, dictate the appropriate key dimensions based on the shaft diameter. These standards consider factors such as material properties, load conditions, and intended application to ensure reliable and safe operation. For instance, a 1-inch diameter shaft might require a 1/4-inch square key according to a specific standard.
Benefits of proper key sizing include reliable power transmission, extended component lifespan, and reduced maintenance costs. Correctly sized keys minimize wear and tear on both the shaft and the hub, leading to longer operating life. This, in turn, reduces the need for frequent replacements and downtime, ultimately lowering maintenance expenses.
Implementing correct keyway sizing involves several steps. First, determine the shaft diameter. Next, consult the relevant standard (e.g., ANSI B17.1) to identify the appropriate key size. Then, ensure the keyway dimensions in both the shaft and hub match the key size. Finally, properly install the key, ensuring a snug fit.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Key Types
There's no single "best" key type. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages:
Best practices for keyway implementation include: proper keyway machining, ensuring a tight fit between the key and keyway, using appropriate lubricants during assembly, regular inspection for wear, and replacing worn keys promptly.
Examples of key applications include: connecting a motor shaft to a pump impeller, securing a gear to a shaft in a gearbox, and joining a pulley to a drive shaft.
Challenges in keyway design include: managing stress concentrations, preventing key slippage, and accommodating variations in shaft and hub tolerances. Solutions involve careful keyway dimensioning, proper key material selection, and precise machining.
Frequently asked questions encompass topics like: How do I determine the correct key size? What are the different types of keys? How do I install a key? What are the common causes of key failure?
Tips and tricks for working with keys include: using a keyway broach for precise keyway cutting, ensuring proper keyway alignment during assembly, and applying anti-seize compound to prevent corrosion.
In conclusion, the seemingly simple shaft key plays a vital role in power transmission. Understanding the relationship between key size and shaft diameter, adhering to established standards, and following best practices are essential for achieving reliable, efficient, and long-lasting performance in rotating machinery. By taking the time to carefully consider keyway design and implementation, engineers can ensure the smooth and uninterrupted operation of critical equipment, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. The precise selection of key dimensions for a given shaft diameter is paramount to avoid failures, ensuring optimal power transfer and longevity of the machinery. Don't underestimate the power of this small component; it truly is the key to success in many engineering applications. Invest time in understanding proper key sizing principles, and your machines will thank you with years of reliable service. Consult relevant standards and resources to gain a deeper understanding and optimize your designs for peak performance.

Standard Inch Shaft Keyway Size Chart | Taqueria Autentica

Drive Shaft Key Sizes at Earl Surrett blog | Taqueria Autentica

Standard Inch Keyway Dimensions Chart | Taqueria Autentica

Shaft Key Catalogue at John Nail blog | Taqueria Autentica

Problem 2 25 points Select a standard square key | Taqueria Autentica

H6 tolerance chart Theoretical Machinist | Taqueria Autentica

Standard Keyways For Metric Shafts at Sharon Paschal blog | Taqueria Autentica

Shaft Key Standard Dimensions at Claude Rondon blog | Taqueria Autentica
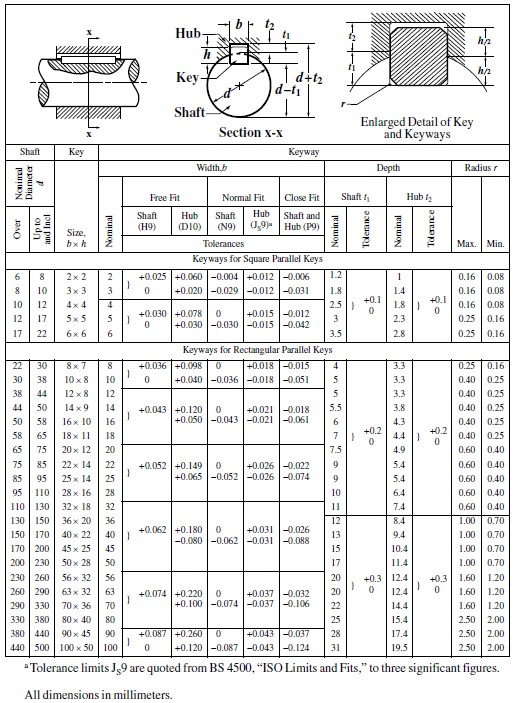
Metric Keyway Shaft Dimensions at Lewis Bleich blog | Taqueria Autentica

ISO Shaft Tolerance Chart | Taqueria Autentica
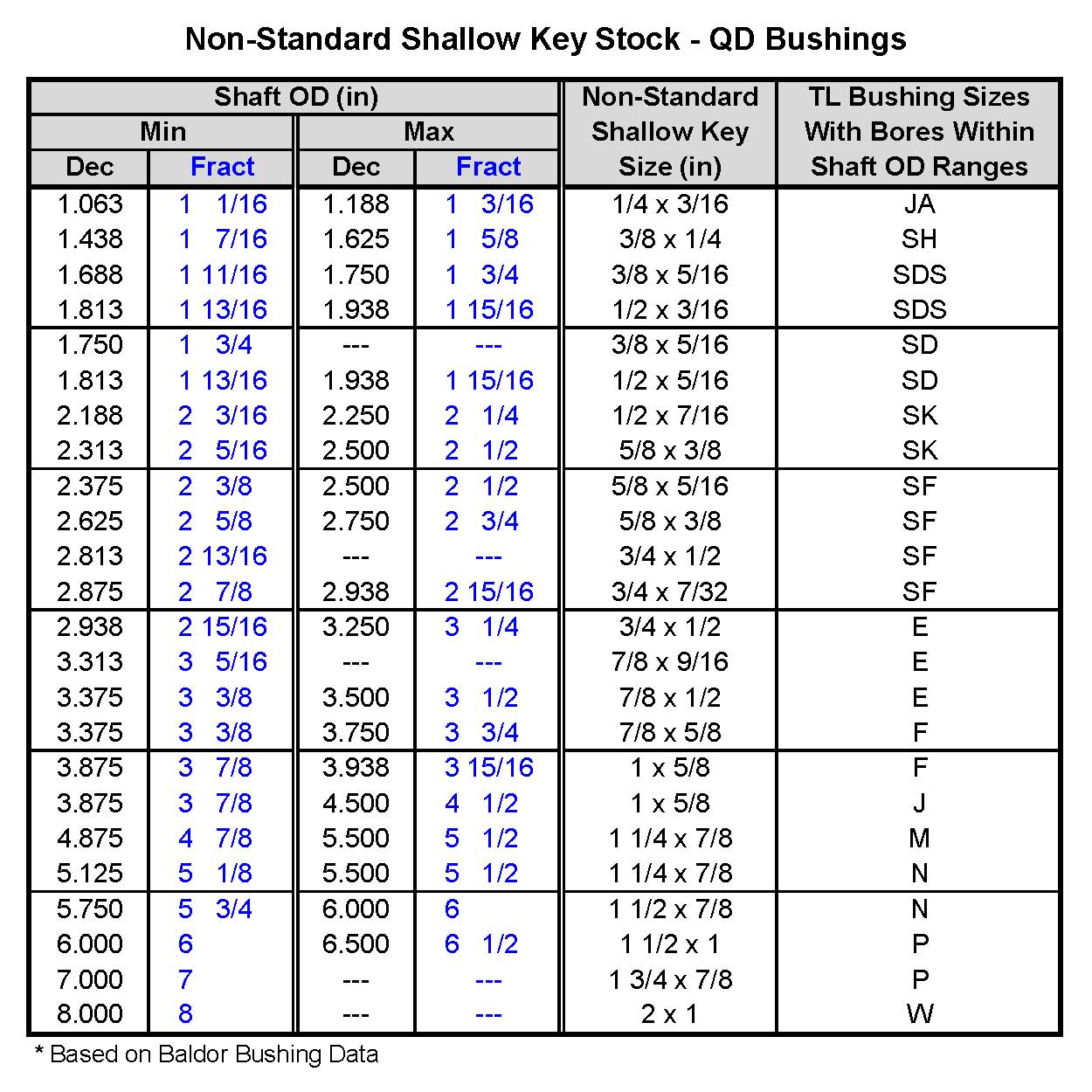
Keyway Shaft Size Chart | Taqueria Autentica

Standard Keyway Size Chart Pdf | Taqueria Autentica