Unlocking the Secrets of Three-Phase Power: The Phasor Diagram Explained
Ever wondered how the electricity that powers our homes and industries is generated and distributed so efficiently? The answer, in large part, lies in the ingenious use of three-phase power systems. And at the heart of understanding these systems is a crucial tool: the three-phase phasor diagram. It's not just a theoretical concept; it's a practical roadmap that engineers and technicians use every day to analyze and troubleshoot electrical circuits.
Three-phase power, unlike single-phase, delivers power in a more consistent, smooth manner. Imagine trying to ride a unicycle versus a tricycle – the latter offers greater stability. Similarly, three-phase power provides a more constant flow of energy, crucial for powering large motors and other industrial equipment. The phasor diagram is the key to visualizing this power flow, representing the three sinusoidal voltages that are 120 degrees out of phase with each other.
Think of a phasor as a rotating vector, a visual representation of a sinusoidal quantity like voltage or current. In a three-phase system, we have three such phasors, offset by 120 degrees, representing the three voltages. The resulting diagram, the three-phase phasor diagram, allows us to easily grasp the relationship between these voltages and analyze the overall system behavior.
The concept of representing alternating current (AC) quantities with phasors arose from the need to simplify complex calculations involving sinusoidal functions. Charles Proteus Steinmetz, a pioneering electrical engineer, is often credited with popularizing the use of phasor diagrams in AC circuit analysis in the late 19th century. His work laid the foundation for understanding and utilizing three-phase power, which became the backbone of modern power distribution.
The importance of the three-phase phasor diagram can't be overstated. It allows engineers to determine the line and phase voltages, currents, and power in a three-phase system. It’s also essential for analyzing unbalanced loads, where the current or voltage in the three phases isn't equal. Understanding these imbalances is crucial for preventing equipment damage and ensuring efficient power distribution.
Analyzing a three-phase phasor diagram involves understanding the relationship between the three phasors representing the voltages or currents. The magnitude of each phasor represents the RMS value of the quantity, and the angle between them represents the phase difference. By adding these phasors vectorially, we can determine the resultant voltage or current.
Benefits of using three-phase phasor diagrams include simplified analysis of complex three-phase circuits, easier visualization of phase relationships, and facilitated calculation of power and other electrical parameters.
A simple example: consider a balanced three-phase system. The phasor diagram will show three equal-length phasors, each separated by 120 degrees. This visual representation immediately confirms the balanced nature of the system.
If the system becomes unbalanced, the phasor diagram will reflect this change. The phasors might have different lengths or unequal angles between them, indicating the imbalance. This visual cue helps engineers quickly identify and address the issue.
One best practice is to always ensure that the phasor diagram is drawn to scale, accurately representing the magnitudes and phase angles of the voltages or currents. Another best practice involves clearly labeling each phasor and indicating the phase sequence.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Three-Phase Phasor Diagrams
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Visual representation simplifies complex relationships | Can be challenging to draw accurately for complex systems |
| Facilitates analysis of balanced and unbalanced loads | Doesn't directly represent transient behavior |
| Helps in understanding motor operation and power flow | Requires understanding of vector addition and phasor concepts |
Frequently Asked Questions about Three-Phase Phasor Diagrams:
1. What is a phasor? - A phasor is a rotating vector representing a sinusoidal quantity.
2. Why are three-phase systems preferred over single-phase? - They provide more constant power delivery and are more efficient for high-power applications.
3. What information can we obtain from a three-phase phasor diagram? - We can determine line and phase voltages, currents, and power.
In conclusion, the three-phase phasor diagram is an indispensable tool for anyone working with three-phase power systems. Its ability to simplify complex relationships, visualize power flow, and aid in troubleshooting makes it essential for engineers, technicians, and students alike. As we continue to rely on three-phase power for our growing energy needs, understanding and utilizing the phasor diagram will remain crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable power distribution. Dive deeper into the world of three-phase power and unlock the full potential of this powerful technology by exploring the resources available online and in technical literature. Mastering the phasor diagram is a key step toward a deeper understanding of the electrical world around us.
three phase phasor diagram | Taqueria Autentica

How To Draw A Phasor Diagram For 3 | Taqueria Autentica

DIAGRAM Single Phase Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

three phase phasor diagram | Taqueria Autentica

DIAGRAM Single Phase Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Delta Three Phase Connection | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram For Three Phase Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

Open Delta Transformer Connection | Taqueria Autentica

Three Phase Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram 3 Phase Star Connection | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram 3 Phase Ac Circuit | Taqueria Autentica

DIAGRAM Single Phase Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica
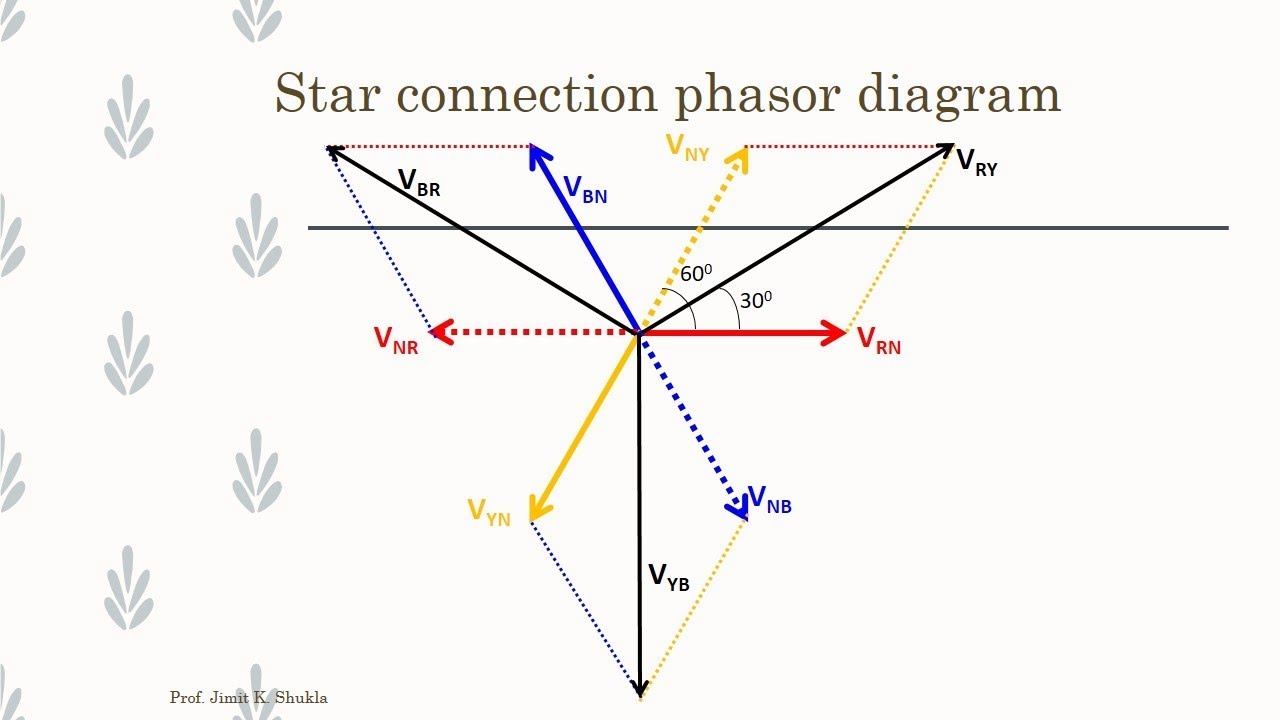
DIAGRAM Single Phase Phasor Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

480v Delta Wye Transformer Wiring Diagram | Taqueria Autentica

Phasor Diagram Of Three Phase Induction Motor | Taqueria Autentica